Data lakes and data warehouses are buzzwords you hear when it comes to data storage in the context of big data goes. In fact, they also refer to two different approaches. The "lake" is actually a coherent term for the data lake: a large basin filled with raw data that is stored there unstructured and without a specific use. A data warehouse, on the other hand, stores structured, filtered data in an organised manner. Which approach should be used for which purpose?
One place to find them all

Companies receive huge amounts of data from a wide variety of sources. They often go beyond what conventional relational databases can handle. Additional systems and tools are needed to manage them.
This creates new insights and reveals trends, making it easier to make decisions based on gut feeling.
All of these data stores have one task: they house data for business reports and analyses. But they differ in their purpose, structure, data types, origin and who has access to them.
The data in these memories often initially comes from systems that generate data CRM, ERPHR, financial applications and other similar applications. The data records created from these systems are partly applied and/or generated according to the rules stored there. They are then stored in a central repository. There they can then be analysed using analysis tools and interpreted in various contexts. This creates new insights and visualises trends, making it easier to make decisions based on gut feeling. Many companies use both a data lake and a data warehouse to cover the spectrum of their data storage requirements.
What is a data lake?
A data lake is a huge repository that stores raw data in its original format. The fact that a data lake can store very different structures is a key feature and advantage. Each stored data element is labelled with a unique identifier and metadata labelled. This means it can be found and assigned again if required. The individual data records usually do not have a predefined purpose. Data is collected more according to a storage principle: what you have, you have.
Data is collected more according to a stock principle: what you have, you have.
There is a lot going on here that is causing many users to migrate to the cloud and the large data storage centres.
Data lakes are typically used by data scientists and engineers who prefer to explore data in its raw form to gain new, unique business insights.
They serve disciplines such as predictive analytics, Machine Learning, Data Visualisation, BI, Big Data Analytics.
The storage costs in a data lake are relatively favourable compared to a data warehouse. Data lakes are also less time-consuming to manage, which reduces operating costs.
What is a data warehouse?
A data warehouse is a repository for data collected and/or generated by business applications for a given purpose. Such applications use a predefined schema to store the data. The data must be cleansed and organised before it is stored in the data warehouse.
As the data stored in a data warehouse is already structured, it is better suited for high-level analyses
As the data stored in a data warehouse is already structured, it is better suited for high-level analyses. BI tools can easily handle the processed data from a data warehouse. This makes it easier for non-data experts to utilise this data in a meaningful way.
The data from a data warehouse can be used to support historical analyses and reports to support decision-making in all areas of a company's business.
Data from a data warehouse is generally accessed by managers and specialist users who need to gain insights into business processes. KPIs want to gain. The data is already structured in such a way that it provides answers to pre-defined questions for the analysis. As a rule, they generate data visualisation, BI analyses and data analytics.
Data warehouses cost more than data lakes and also require more time to manage, which leads to additional operating costs.

Data quality & AI : AI can only be as good as your data
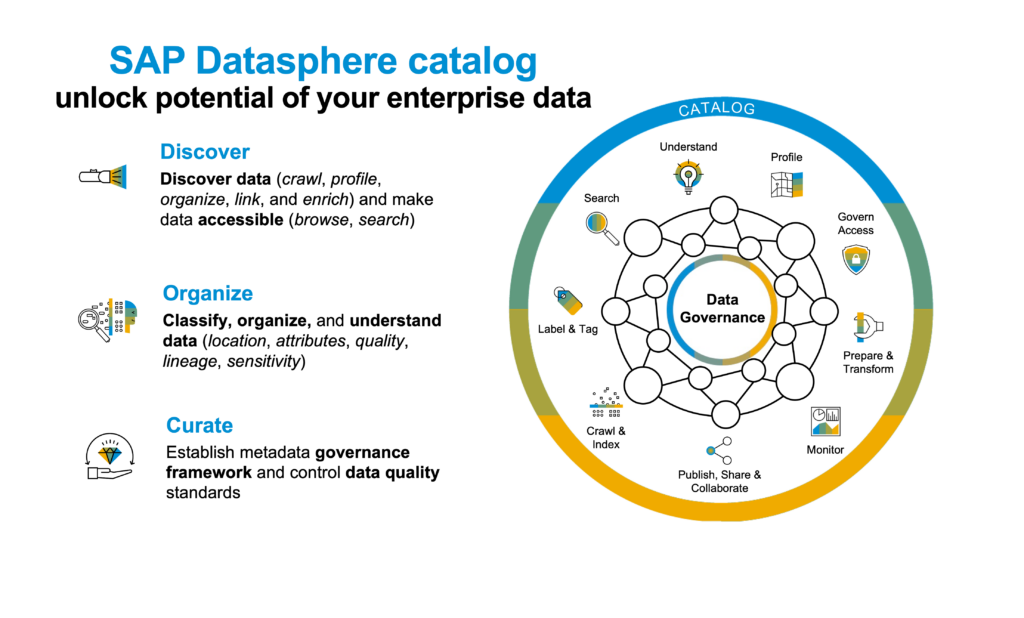
SAP tools for integration & data analysis 2023

Dashboard functions in MARIProject

More key figures transparency in the ERP system

Data warehouse or data lake


