On 11 March 2025, with the adoption of ViDA (VAT in the Digital Age) one of the most ambitious reform packages of the European VAT system. With ViDA, the EU is creating a future-proof set of rules for the value added tax - with a particular focus on digitalisation, efficiency and fraud prevention. For SMEs, the reform brings far-reaching changes, but also clear opportunities.
Why ViDA? A system under pressure
The EU has been struggling for years with an immense Sales tax gap - the difference between theoretical tax revenue and actual figures. In 2020, this gap amounted to around 99 billion euros. Intra-Community trade in particular is considered a gateway for systematic tax fraud. ViDA is the concrete answer to these challenges.
At the same time, ViDA reflects the reality of today's economy: platform models, real-time communication and increasing internationalisation are challenging traditional taxation logic. VAT must therefore not only become more secure, but also more digital.
The three pillars of ViDA
1. digital reporting and e-billing (DRR)
Probably the most significant aspect: the introduction of a standardised, structured e-invoicing standards and the mandatory reporting of transaction data in near real time. Already from 14 April 2025 Member States may make B2B e-invoices mandatory even without the authorisation of the EU Council.
By 2030, electronic invoices in a structured format (in accordance with EN 16931) will be mandatory for intra-Community B2B services and deliveries. Traditional formats such as PDF or JPEG will therefore lose their status as legally valid invoices.
At the same time, the Digital Reporting Requirement (DRR) introduced a system that Summarised message (EC Sales List). In future, companies must complete transactions within 10 days after the controllable event - a paradigm shift towards real-time control.
2. new rules for the platform economy
Platform operator in the area of Short-term letting and Passenger transport have to be paid from 1 July 2028 as „Deemed Supplier“ - in other words, they are considered to be the provider of the service for tax purposes. This means that platforms are held more accountable and are also more transparent for tax purposes.
For platform companies with an international reach in particular, this means more complexity - but also clarity about their tax obligations within the EU.
3. single VAT registration (SVR)
From July 2028, the standardised VAT registration (Single VAT Registration) has been significantly expanded. In future, companies will be able to register in only an EU Member State and register via the extended OSS/IOSS systems handle all tax obligations in the EU.
For SMEs that previously struggled with complex multiple registrations, this is a clear step towards Reducing bureaucracy.
Timetable: What companies need to know now
| date | Range | Relevant change |
|---|---|---|
| 14 April 2025 | E-invoicing | National mandatory systems permitted without EU authorisation. Consent of the recipient no longer required. |
| 1 July 2028 | Platform economy / SVR | Platforms as Deemed Supplier. Extension of the SVR regulations. |
| 1 July 2030 | E-bill & DRR | Mandatory structured e-invoices and real-time reporting of intra-Community B2B transactions. |
| 1 January 2035 | Harmonisation | National DRR systems must be compatible with EU requirements. |
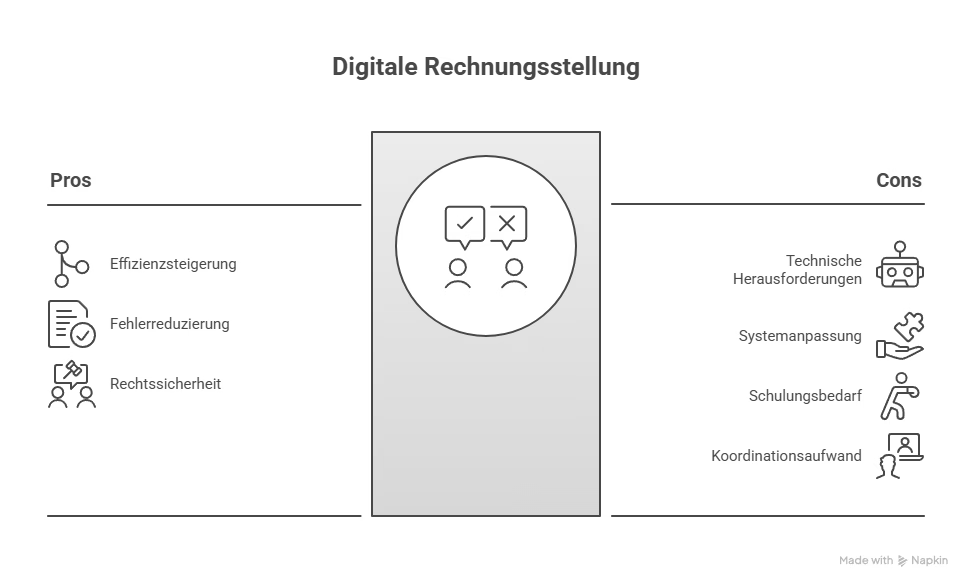
Effects on the SME sector
Opportunities:
- Standardisation and automation of invoicing processes reduce the administrative burden in the long term.
- Fewer sources of error through digital processing.
- Reduced need for tax registrations in several countries.
- Clearer obligations for platform operators lead to more legal certainty.
Challenges:
- Conversion to new technical standards (e.g. XML-based formats in accordance with EN 16931).
- Adjustment of the ERP- and accounting systems to DRR interfaces.
- Training employees in dealing with new processes and deadlines.
- Coordination with IT partners to implement all requirements on time.
Recommendations for companies
- Carry out a system checkDoes the current ERP system support structured e-invoices in accordance with EN 16931?
- Integrate software partnersERP provider and tax consultant should be involved at an early stage to ensure DRR and e-invoicing compatibility.
- Define and digitalise processesAnalogue or manual processes hinder timely data reporting - process automation is mandatory.
- Take deadlines seriouslyIn particular, the 10-day period after the taxable event will pose an organisational challenge for many companies.
- Clarify communication internallyWho is responsible for the creation, approval and transmission of the e-bill?
ViDA becomes a game changer
ViDA does not merely bring cosmetic changes, but a Structural reform of VAT in Europe. While the transitional periods appear long at first glance, the Technical and organisational preparatory work should not be underestimated - especially for medium-sized companies with established system landscapes.
However, the switch to e-invoicing and DRR is not only a regulatory obligation, but also an opportunity, streamline digital business processes, Avoid fraud and at the same time simplify international tax processing.
Verifactu in Spain: the new invoicing obligation

The e-invoicing regulations in Europe

E-bill 2025 FAQs

Preparation for the introduction of CKS.EINVOICE

E-invoicing - The flexible EN 16931 standard

E-Invoice master data and settings in SAP Business One

Archiving of e-invoices

International e-invoices: differences and global developments

MariProject / Tool for e-invoicing



